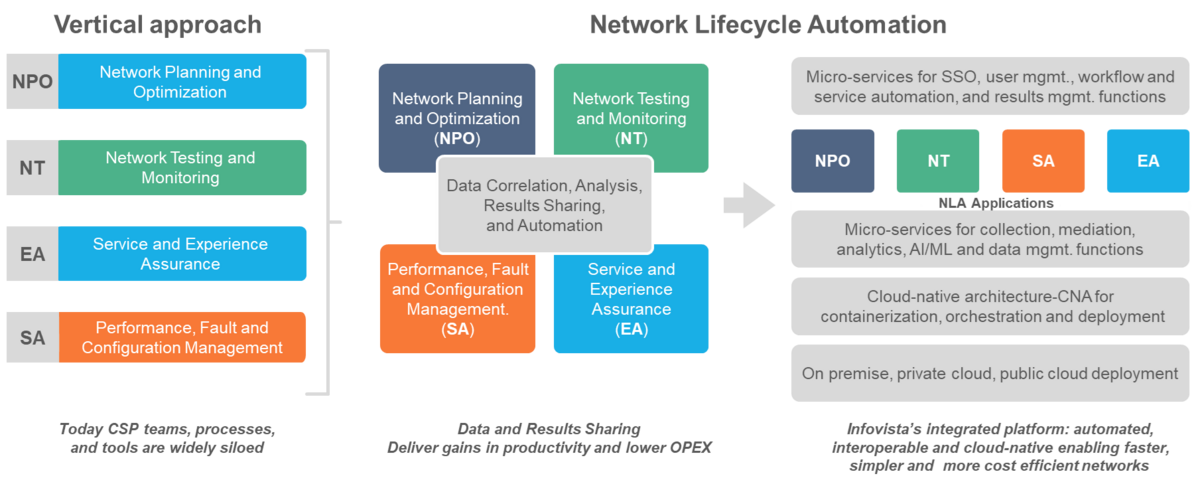
In the era of cloudification, a new, holistic approach to continuous planning, deployment, operation, and monetization is urgently needed: Network Lifecycle Automation (NLA). Get it right, and CAPEX, OPEX and TTM benefits promised by 5G are finally within grasp.
In a recent TM Forum survey and report, ‘Can CSPs Optimize 5G Investments?’, the results demonstrate a consensus among global CSPs, about 5G expectations versus reality: that the benefits of 5G are taking longer than expected to materialize. This is not because of roll-out delays, nor is it because of roll-out overspend, it’s because of a lack of network lifecycle automation capability. The most common priority for CSPs to unblock the realization of the full potential is to ‘establish a common platform for automation between planning, deployment and operations systems’. In other words, to enable network lifecycle automation (NLA).
NLA maximizes the value of cloudification
5G, along with cloudified network technologies in general, presents a significant challenge to the CSP today. Planning, deploying and operating a cloudified network is highly complex and mission-critical. But more importantly, it has to become continuous and simultaneous, as opposed to a linear sequence of phases with a start and an end. This is because of network programmability. The ability to deploy, configure and operate virtualized network elements remotely and dynamically, meaning planning (and replanning), deployment and testing, have joined operations to become continuous processes.
Getting the most out of the network capacity available to a CSP – for example by delivering higher value services such as those backed by SLA guarantees (and multiple, diverse services at the same time, at scale) – requires continuous network replanning and optimization, deployment and testing, and automated assurance & operations.
Critically though, it also requires these three commonly separate disciplines to interoperate, to realize holistic machine learning and artificial intelligence-driven multi-phase automation use cases. Network planning informs the optimal routes and activities for network testing; test results validate or adjust planning predictive algorithms; customer preferences and utilization trends support ROI-driven planning; and so on.
NLA use cases and business outcomes
So, what are some of the potential benefits to the CSP of Network Lifecycle Automation that have brought this topic so high up on the agenda today?
Optimizing ROI:
Combining operational intelligence about customer experience and network performance with planning intelligence about network coverage and throughput, enables the CSP to optimize RAN and backhaul planning and configuration for optimal ROI. This delivers churn reduction and increased revenue potential to complete the ROI picture.
Improving Customer Experience and NPS:
360° Assurance combines customer experience intelligence with application and network intelligence, with automated root-cause analysis, customer impact analysis, and workflow automation to resolve network issues before they impact customer experience. The aforementioned TM Forum survey showed that improving customer experience and NPS is the most important business outcome expected from the adoption of network lifecycle automation.
Reducing drive test and walk test time and effort:
Using planning ‘sweet spot’ data to inform automated routing and guided workflows for drive testing and walk testing. This holistic approach to ‘precision drive testing’ can reduce time, scope and cost by over 70%.
Accelerating time-to-market:
Data-driven service go-to-market can be enabled by combining intelligence into the network capacity available to launch a given service with the support of active testing for the rapid validation of service feasibility and service acceptance along with automated assurance and operations. This provides the intelligence needed for rapid decision-making in the roll-out of new services, the confidence that service SLA guarantees can be delivered, and the insights needed to make precise capacity expansion investments to fulfil expected future demand.
We know that this is not something that can be achieved overnight. Indeed, in the TM Forum’s global survey many CSPs reported they have been working on enabling multi-phase automation use cases such as these for some time, but one thing that is clear, is there is no standard approach or framework that encapsulates network lifecycle automation. Not yet.
The platform prerequisites of NLA
In its survey, TM Forum found that CSPs’ strategies for establishing a network lifecycle automation capability are diverse, ranging from in-house development to working with network vendors’ service offerings. A large majority of respondents, however, think the solution should involve working with multiple vendors in some capacity, which implies a requirement for interoperability across multiple applications.
This brings several prerequisites into the equation. There needs to be, at a minimum, common analytics engines; common automation engines; common open APIs and network connectors; and common user and developer resources. This is not to mention the table stakes of advanced cloud-native architecture to support critical capabilities like distributed deployments and scalability to cost-efficiently handle fluctuating workloads, and multi-tenancy for enterprise self-service portals to deliver monetizable and differentiated services. Some of these are described in more detail below:
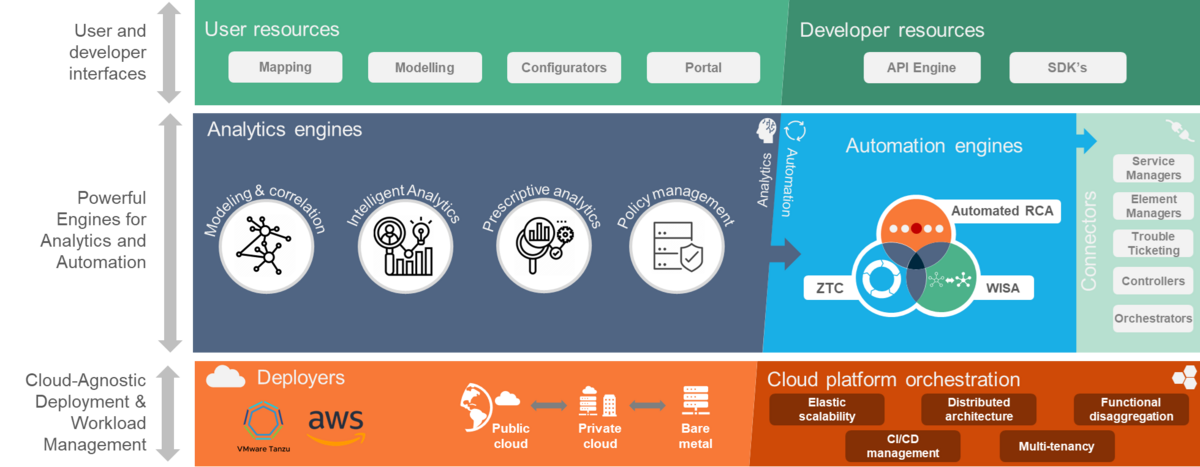
Common analytics engines:
To enable network lifecycle automation use cases, the supporting applications should draw from a common set of analytics engines, supporting modeling, correlation and prediction, with advanced AI/ML for scenario analysis and intelligent prioritization as examples. In this way, it’s possible to derive ‘multi-phase’ insights, like the sensitivity of different customer segments to network reliability across regions.
Common automation engines:
Automation across the network lifecycle takes different forms. Multi-phase process automation across applications is challenging and difficult to scale unless they share the same process automation engine. Automated network configuration and orchestration is critical to closing the loop but shouldn’t be limited only to the operations domain. It should be possible, for example, to trigger a network configuration in response to anomalies observed in drive testing, even if there is no live traffic running across the network. Automated what-if scenario analysis (with a digital twin) can have applications across planning, deployment and operations.
Common APIs and Network Connectors:
Network lifecycle automation brings together insights from different phases of the network lifecycle (network planning & optimization, testing & deployment, and operations). Interoperability for data exchange across the applications is essential for this to work. But so is data exchange with external systems. Take CAPEX allocation as an example: Smart CAPEX allocation requires planning applications to systematically ingest data from assurance applications to make accurate predictions of network performance and customer experience under different conditions. But it also needs business data (pricing, ARPU, churn risk) from external systems such as CRM.
Common User and Developer Resources:
With technologies such as AI and ML and extensive automation being core capabilities for network lifecycle automation, it’s essential that a broad user community can interact with the system, through common mapping, modeling, configuration, filtering, reporting and dashboarding interfaces. Similarly, use case co-creation requires common developer resources like SDKs, with microservices-based application architecture to support agile DevOps.
Making NLA a reality
Building and deploying NLA is a collaborative effort. We build end-to-end outcome-based NLA solutions that deliver the maximum benefits to customers, whom we listen to and work with closely throughout the process: validating, localizing, fine-tuning and optimizing. Our NLA Cloud Platform, which powers NLA solutions like Infovista Smart CAPEX, is shared across our entire applications portfolio, and deployable on public, private, hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
Infovista continues to deliver new, innovative NLA solutions, each designed to address a specific, significant challenge or opportunity for a broad set of stakeholders, across technology and business teams in the CSP organization.
Get in touch to learn more about our NLA vision, platform and solutions and how NLA can help your business today. You can find out more about NLA with Infovista.



